Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory
Cardiac Catheterization is a medical procedure that cardiologists (heart specialists) use to evaluate heart function and diagnose cardiovascular conditions. Lorma has inaugurated its Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory this March 2016. Patients from the North, who are suffering from Cardiac diseases, need not go to Manila to undergo cardiac procedures as they can come to Lorma Medical Center.
The Lorma Cathlab is the first and only cardiac lab unit in Region 1. The Unit is able to do cardiac and vascular procedures.
Cardiac Procedures:
•Coronary Angiography
This test is to check for blockages in the arteries leading to your heart. A dye will be injected through the catheter, and X-ray images of your heart arteries will be taken. In a coronary angiogram, the catheter is usually first placed in the artery in your groin or wrist.
•Coronary Angioplasty or Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
This procedure is used to open a narrowed artery in or near your heart. The catheter can be inserted in either your wrist or groin for this procedure.
A long, flexible catheter will be threaded through your arteries to the narrowed artery. Then, a smaller balloon catheter will be fed through the flexible catheter and inflated at the narrowed area to open it. In many cases, your doctor will also place a mesh coil called a stent at the narrowed portion to help keep the artery open.
•Intra-aortic Baloon Pump Insertion (IABP)
An intra-aortic balloon pump, or IABP, is a long, skinny balloon that controls the flow of blood through your largest blood vessel, the aorta. The device gets smaller when your heart pumps so blood can flow out to the rest of your body. Then it gets bigger when your heart relaxes to keep more blood in your heart.
•Intra-aortic Baloon Pump Insertion (IABP)
An ICD is a battery-powered device placed under the skin that keeps track of your heart rate. Thin wires connect the ICD to your heart. If an abnormal heart rhythm is detected the device will deliver an electric shock to restore a normal heartbeat if your heart is beating chaotically and much too fast.
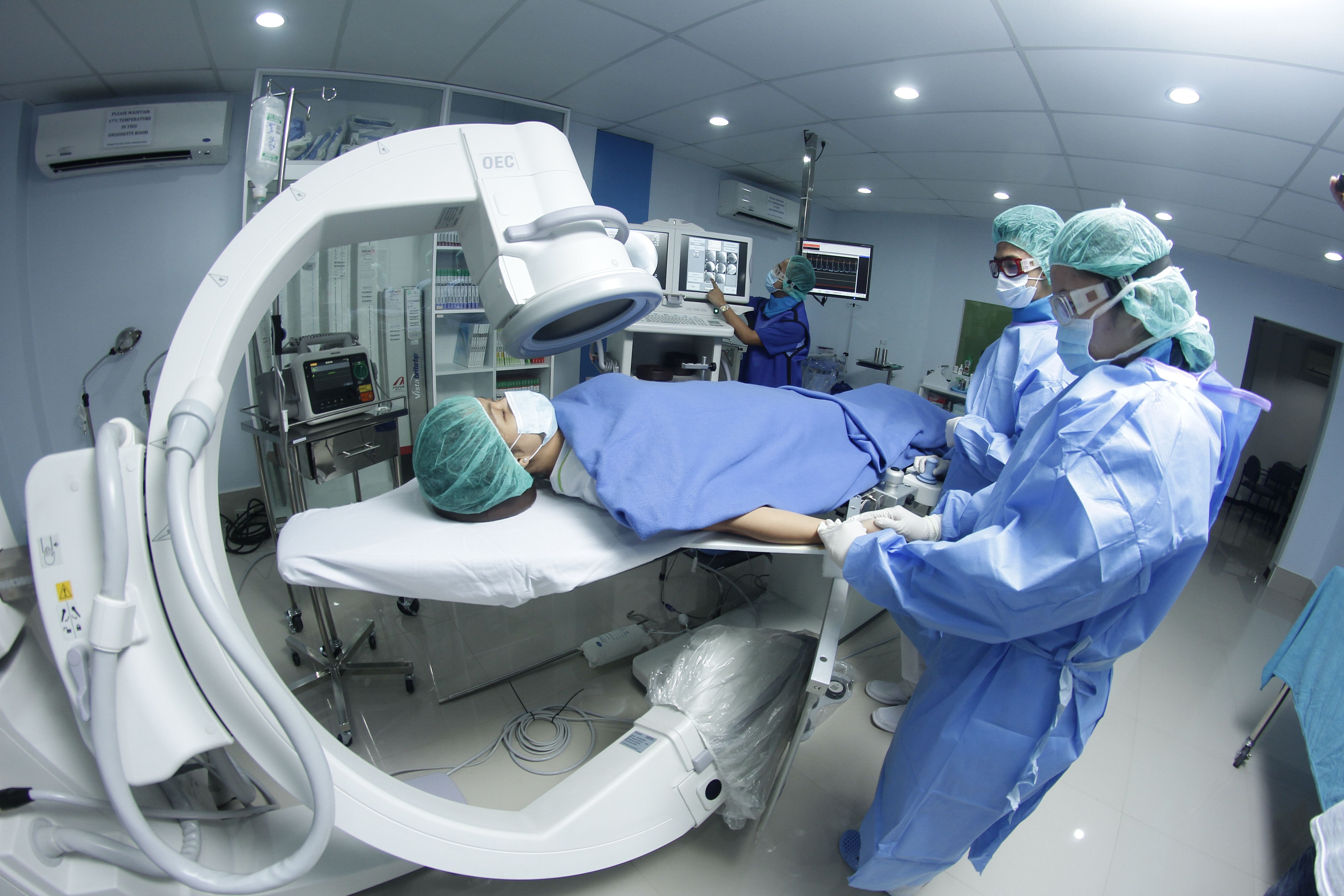
•Permanent and Temporary Pacemaker Insertion
A pacemaker insertion is the implantation of a small electronic device that is usually placed in the chest (just below the collarbone) to help regulate slow electrical problems with the heart. A pacemaker may be recommended to ensure that the heartbeat does not slow to a dangerously low rate.
•Hemodynamic Studies
Hemodynamics is the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, such as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. Hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Thus hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels.
Radiology Procedures:
•Cerebral Angiogram
Cerebral angiography is a diagnostic test that uses an X-ray. It produces a cerebral angiogram, or an image that can help your doctor find blockages or other abnormalities in the blood vessels of your head and neck. Blockages or abnormalities can lead to a stroke or bleeding in the brain.
Interventional Radiology Procedures:
•Coiling of Aneurysm
This is a procedure performed to block blood flow into an aneurysm (a weakened area in the wall of an artery).
Endovascular coiling is a minimally invasive technique, which means an incision in the skull is not required to treat the brain aneurysm. Rather, a catheter is used to reach the aneurysm in the brain.
During endovascular coiling, a catheter is passed through the groin up into the artery containing the aneurysm. Platinum coils are then released. The coils induce clotting of the aneurysm and, in this way, prevent blood from getting into it.
•Chemoembolization
This is an interventional radiology procedure designed to reduce blood supply to a tumor and deliver chemotherapy drugs directly to a tumor, while reducing exposure to healthy tissues. This procedure reduces the side effects of chemotherapy while killing cancer cells.
•Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage
Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage is a procedure where a small, flexible, plastic tube is placed through the skin into the liver in order to drain an obstructed bile duct system.
The Cathlab has a recovery room for patients recovering from the direct effects of anesthesia and for monitoring of post-surgical complications. From the recovery room, patients are transferred to the coronary care unit for close monitoring.
The Lorma Cathlab is a joint partnership of the HB Calleja National Heart Institutes and the Lorma Heart Institute. The Cathlab team is composed of well-trained and experienced nurses, radiologists and interventional cardiologists, Dr. Lala Ann F. Bambico, FPCP, FPCC, Dr. Romeo G. Molano, Jr., FPCP, FPCC, and Dr. Justina S. Calibuso, FPCP.
For more inquiries, contact the Cathlab Manager, Ms. Shaia Marie B. Mayo, RN, MAN at 072-700-0000 local 219 and 229.
